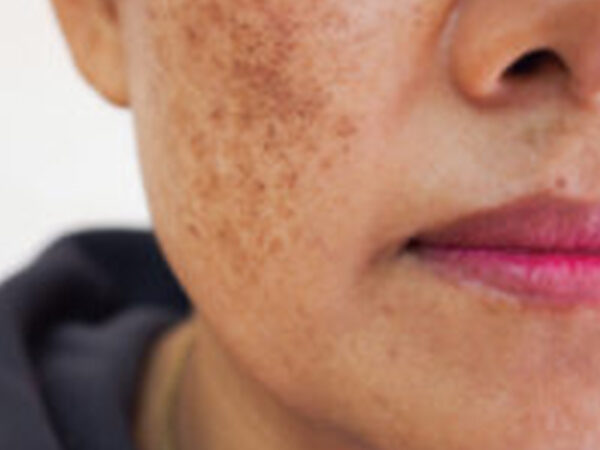
Melasma is a common skin condition that affects many people, especially women. It is a chronic condition that causes dark, discolored patches on the skin, typically on the face, but also can occur on other parts of the body. While the exact cause of melasma is not known, it is often linked to hormonal changes, sun exposure, and genetics.
If you’re looking for information, you’ve come to the right place. In this article, we’ll explore everything that is currently known, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment.
What is Melasma?
It is a skin condition that causes dark, discolored patches on the skin. The patches typically appear on the cheeks, forehead, upper lip, and nose. It is most common in women, particularly those who are pregnant or taking hormonal contraceptives. However, it can also affect men and non-pregnant women.
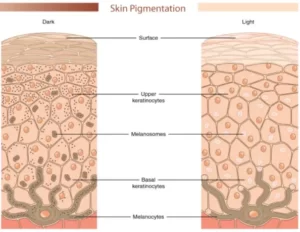
Causes of Melasma:
The exact cause is not known, but it is believed to be linked to hormonal changes, sun exposure, and genetics. Some of the common triggers of include:
- Hormonal changes: Melasma is most common in women who are pregnant or taking hormonal contraceptives. Hormonal changes can trigger the production of melanin, which causes the skin to darken.
- Sun exposure: Exposure to the sun’s UV rays can trigger the production of melanin, causing the skin to darken. This is why melasma is more common in people who live in sunny climates.
- Genetics: If you have a family history of melasma, you are more likely to develop the condition.
The cause of melasma mot likely involves a complex interplay between melanocytes, keratinocytes, and inflammatory cells. Melanocytes produce melanin, which is then transferred to nearby keratinocytes, the cells that make up the outer layer of the skin. In melasma, the melanocytes become overactive and produce too much melanin, leading to the formation of dark patches on the skin.
In addition to the overproduction of melanin, there is also evidence of increased inflammation in the skin of patients with melasma. This inflammation may be triggered by UV exposure or other environmental factors and can contribute to the development and persistence of the condition.
While the exact pathophysiology of melasma is not fully understood, research has identified several key factors that contribute to its development. By understanding these factors, researchers and clinicians can develop more effective treatments for this common and often frustrating skin condition.
Symptoms of Melasma:
The most common symptom of melasma is dark, discolored patches on the skin. The patches are usually brown or gray-brown in color and typically appear on the cheeks, forehead, upper lip, and nose. Melasma can also occur on other parts of the body that are exposed to the sun, such as the neck and arms.
Interesting Facts:
- It is more common in women than in men, and is often referred to as the “mask of pregnancy” due to its prevalence in pregnant women.
- It is most common in people with darker skin types, including those of African, Asian, and Hispanic descent.
- The most common locations for it to appear on the face are the cheeks, forehead, upper lip, and chin.
- It can also occur on other parts of the body that are exposed to the sun, such as the neck, chest, and arms.
- There is no cure, but there are several treatment options available that can help reduce the appearance of dark spots, including topical creams, chemical peels, and laser therapy.
- In addition to sun exposure and hormonal changes, other factors that can trigger it include stress, heat, and certain medications.
- It can be a frustrating and stubborn condition to treat, and it may take several months of consistent treatment to see noticeable improvements in the appearance of the skin.
- The use of high-powered lasers or other aggressive treatments can sometimes worsen melasma, so it is important to work with a qualified dermatologist to develop a safe and effective treatment plan.
- In some cases, melasma may fade on its own over time, particularly after hormonal changes have subsided, such as after pregnancy or the cessation of hormonal contraceptives.
- In addition to topical treatments and sun protection, certain lifestyle changes, such as managing stress and getting enough sleep, may also help to improve the appearance of melasma.
Diagnosis of Melasma:
If you suspect that you have melasma, it is important to see a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis. Your skincare professional will examine your skin and may use a special device called a Wood’s lamp to look for signs of melasma. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
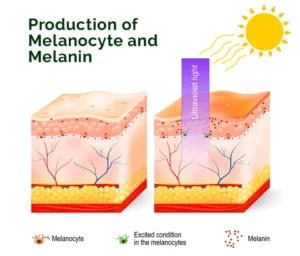
Treatment of Melasma
While there is no cure for melasma, there are several treatment options available that can help reduce the appearance of the dark, discolored patches. Some of the most common treatment options include:
- Sunscreen:
- One of the most effective ways to prevent melasma is to protect your skin from the sun’s harmful UV rays. Sunscreen is an essential part of any treatment plan for melasma, as exposure to sunlight can worsen the condition. Look for a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, and apply it generously to all exposed areas of your skin.
- Vitamin C:
- Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that can help to brighten the skin and reduce the appearance of dark spots. It works by inhibiting the production of melanin, the pigment that gives color to our skin. In addition to its skin-lightening properties, vitamin C also helps to protect the skin from environmental stressors and supports collagen production, which can improve the overall texture and appearance of the skin.
- Kojic Acid:
- Kojic acid is a natural ingredient that is often used in skin care products to reduce the appearance of dark spots and hyperpigmentation. It works by inhibiting the production of tyrosinase, the enzyme responsible for the production of melanin. Kojic acid is often used in combination with other skin-lightening ingredients, such as vitamin C and hydroxy acids, to enhance its effectiveness.
- Azelaic Acid:
- Azelaic acid is a naturally occurring acid that is found in grains like wheat, rye, and barley. It has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, making it an effective treatment for a variety of skin conditions, including acne and rosacea. Azelaic acid also helps to reduce the production of melanin, making it a useful ingredient in the treatment of melasma.
- Niacinamide:
- Niacinamide, also known as vitamin B3, is a powerful ingredient that has a wide range of benefits for the skin. It has been shown to reduce the production of melanin, making it an effective treatment for hyperpigmentation and melasma. Niacinamide also helps to improve the overall texture and tone of the skin, reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and support the skin’s natural barrier function.
- Glycolic Acid:
- Glycolic acid is an alpha-hydroxy acid that is commonly used in skin care products to exfoliate the skin and improve its texture. It works by breaking down the bonds between dead skin cells, allowing them to be easily removed from the surface of the skin. In addition to its exfoliating properties, glycolic acid also helps to reduce the production of melanin, making it an effective treatment for melasma.
- Licorice Root Extract:
- Licorice root extract is a natural ingredient that has been used for centuries in traditional medicine. It has anti-inflammatory and skin-lightening properties, making it an effective treatment for a variety of skin conditions, including melasma. Licorice root extract works by inhibiting the production of tyrosinase, the enzyme responsible for the production of melanin.
- Retinoids:
- Retinoids are a class of vitamin A derivatives that are commonly used in skin care products to improve the texture and tone of the skin. They work by increasing cell turnover and stimulating collagen production, which can help to reduce the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation. Retinoids are also effective in the treatment of melasma, as they help to reduce the production of melanin and improve the overall texture and tone of the skin.
- Tranexamic Acid:
- Tranexamic acid is a medication that is commonly used to treat heavy bleeding. However, it has also been found to be effective in the treatment of melasma. Tranexamic acid works by inhibiting the production of plasmin, an enzyme that can trigger the production of melanin. It has been shown to be effective in reducing the appearance of dark spots and hyperpigmentation in patients with melasma.
- Vitamin E:
- Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that can help to protect the skin from environmental stressors and free radicals that can damage the skin. It also has skin-lightening properties, making it an effective ingredient in the treatment of melasma. Vitamin E works by inhibiting the production of melanin and reducing inflammation in the skin. It is often used in combination with other active ingredients, such as vitamin C and kojic acid, to enhance its effectiveness.

Best Sellers:
- Mesoestetic Melan Tran3X Kit
- Neoretin Serum Booster & Neoretin GelCream Pack
- DermExcel Treatment Packs: Pigmentation
In conclusion, there are several active ingredients that are used in the treatment of melasma, each with its own unique properties and benefits. These ingredients work by inhibiting the production of melanin, exfoliating the skin, and improving its texture and tone. When selecting skin care products for the treatment of melasma, it is important to look for products that contain these active ingredients and to use them as directed for best results. In addition, it is important to protect the skin from the sun’s harmful UV rays with a broad-spectrum sunscreen and to avoid other triggers, such as hormonal changes and stress, that can worsen the condition.
Shop Melasma Products HERE.
